Lab: Intro to Asynchronous Serial Communications
October 14, 2020
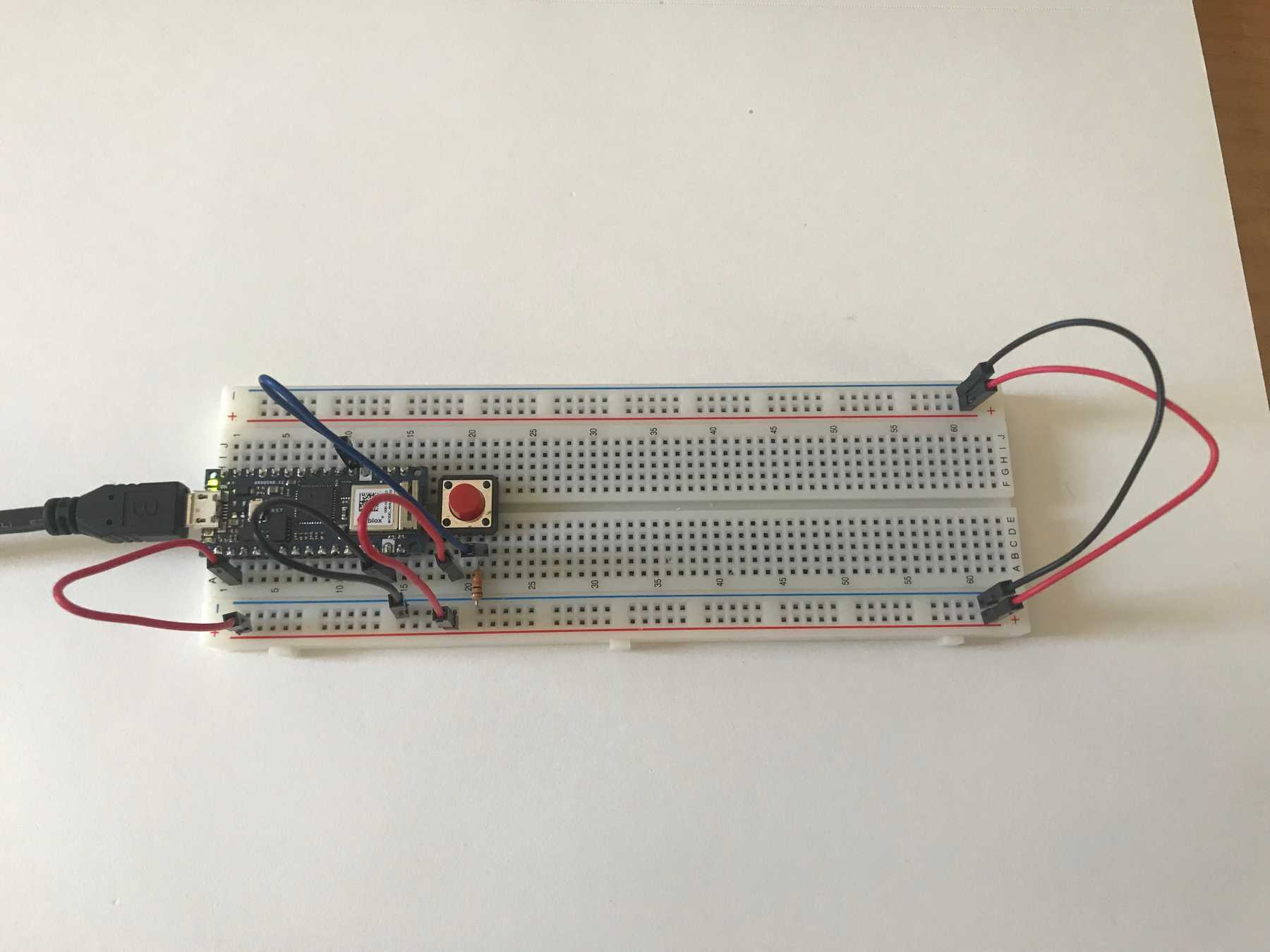
Physical ComputingIn this lab I learned the basics of interfacing Arduino code with other programs via serial communication.
I used the accelerometer in the Arduino so I only needed to wire up a pushbutton to the controller.
I experimented with viewing the Serial stream in the terminal via cat, as well as with different output formats (Binary, Hex, and Octal). I then implemented a two way communication so that the Arduino waits for serial input before sending output. The following code begins sending accelerometer data when it receives any sort of serial input.
#include "Arduino_LSM6DS3.h"
const int BUTTON_PIN = 2;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
if (!IMU.begin()) {
Serial.println("Failed to initialize IMU");
// stop here if you can't access the IMU:
while (true);
}
while (Serial.available() <= 0) {
Serial.println("hello"); // send a starting message
delay(300); // wait 1/3 second
}
}
void loop() {
// values for acceleration and rotation:
float xAcc, yAcc, zAcc;
float xGyro, yGyro, zGyro;
// if both accelerometer and gyrometer are ready to be read:
if (IMU.accelerationAvailable() &&
IMU.gyroscopeAvailable()) {
// read accelerometer and gyrometer:
IMU.readAcceleration(xAcc, yAcc, zAcc);
// print the results:
IMU.readGyroscope(xGyro, yGyro, zGyro);
Serial.print(xAcc);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(yAcc);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(zAcc);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(xGyro);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(yGyro);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.println(zGyro);
}
}Here it is in action:
Two-way Serial Communication